The endocrine system is a network of glands that secrete hormones directly into the blood. These hormones regulate growth, metabolism, reproduction, and many vital body functions. Unlike exocrine glands, they do not have ducts → they are called ductless glands.
1. Pituitary Gland – Master Gland
- Location: Base of the brain, below hypothalamus.
- Divisions: Anterior lobe, Posterior lobe.
Hormones & Functions:
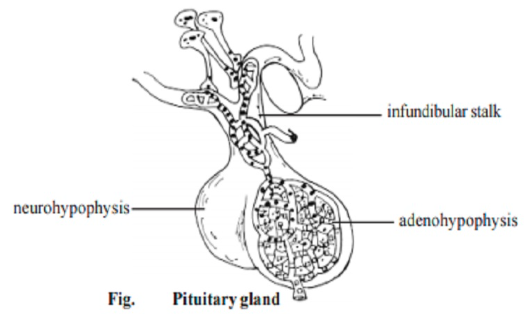
- Anterior lobe (adenohypophysis):
- Growth hormone (GH) → growth of bones & muscles.
- TSH (Thyroid Stimulating Hormone) → stimulates thyroid.
- ACTH (Adrenocorticotropic Hormone) → stimulates adrenal cortex.
- FSH & LH → control reproductive functions.
- Prolactin → stimulates milk production.
- Posterior lobe (neurohypophysis):
- ADH (Antidiuretic Hormone) → water balance (reabsorbs water in kidneys).
- Oxytocin → contraction of uterus during childbirth, milk ejection.
2. Thyroid Gland
- Location: Neck, in front of trachea.
- Hormones:
- Thyroxine (T₄) & Triiodothyronine (T₃) → regulate metabolism, growth, development.
- Calcitonin → lowers blood calcium.
- Disorders:
- Goiter (enlargement due to iodine deficiency).
- Hyperthyroidism → weight loss, anxiety.
- Hypothyroidism → weight gain, lethargy, cretinism in children.
3. Parathyroid Glands
- Location: 4 small glands on the back of thyroid.
- Hormone:
- Parathyroid Hormone (PTH) → increases blood calcium by breaking down bone.
4. Adrenal Glands – Emergency Glands
- Location: On top of each kidney.
- Parts: Cortex & Medulla.
Cortex (outer):
- Cortisol → stress hormone, regulates metabolism.
- Aldosterone → maintains sodium & potassium balance.
- Sex hormones (small amounts).
Medulla (inner):
- Adrenaline (epinephrine) → “fight or flight” response.
- Noradrenaline → maintains blood pressure.
5. Pancreas (Islets of Langerhans)
- Location: Behind stomach.
- Hormones:
- Insulin → lowers blood sugar (stores glucose as glycogen).
- Glucagon → raises blood sugar (breaks down glycogen).
- Disorder: Diabetes mellitus (insulin deficiency).
7. Thymus Gland
- Location: Behind sternum, in chest (large in children, shrinks in adults).
- Hormone:
- Thymosin → development of immune system (T-lymphocytes).
8. Gonads (Sex Glands)
Testes (in males):
- Testosterone → male secondary sexual characters, sperm production.
Ovaries (in females):
- Estrogen → female secondary sexual characters, menstrual cycle.
- Progesterone → prepares uterus for pregnancy.
Summary Table
| Gland | Hormones Secreted | Major Functions |
|---|---|---|
| Pituitary | GH, TSH, ACTH, FSH, LH, Prolactin, ADH, Oxytocin | Master control of other glands, growth, reproduction |
| Thyroid | T₃, T₄, Calcitonin | Metabolism, growth, calcium regulation |
| Parathyroid | PTH | Increases blood calcium |
| Adrenal | Cortisol, Aldosterone, Adrenaline, Noradrenaline | Stress response, metabolism, water balance |
| Pancreas | Insulin, Glucagon | Blood sugar regulation |
| Pineal | Melatonin | Sleep-wake cycle |
| Thymus | Thymosin | Immunity development |
| Testes | Testosterone | Male reproduction |
| Ovaries | Estrogen, Progesterone | Female reproduction |
Human Endocrine Glands
